

Some functional groups in consumer productsBENGAYCamphor a ketoneMenthol an alcoholMethyl salicylate an ester and a phenolNeopsporin Miconazole many functional groups (ether, chloro)Dimethyl ether propellentHalls coughMenthol- an alcohol O O 4) CH3COH 5) CH3COCH3 carboxylic acid ester Solution1)CH3CH2CH2OHalcohol2) CH3OCH2CH3 ether3) CH3CH2NH2amine Learning CheckClassify each of the following as: alcohol, ether, aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, ester, amine or amide.1)CH3CH2CH2OH2) CH3OCH2CH33) CH3CH2NH2 In amides, the hydroxyl group of a carboxylic acid is replaced by a nitrogen group.Copyright 2005 by Pearson Education, Inc.Publishing as Benjamin Cummingsįunctional GroupsCopyright 2005 by Pearson Education, Inc.Publishing as Benjamin Cummings O COHAn ester contains the carboxyl group between carbon atoms.Copyright 2005 by Pearson Education, Inc.Publishing as Benjamin CummingsĪmines and AmidesIn amines, the functional group is a nitrogen atom. In a ketone, the carbon of the carbonyl group is attached to two other carbon atoms.Copyright 2005 by Pearson Education, Inc.Publishing as Benjamin CummingsĬarboxylic Acids and EstersCarboxylic acids contain the carboxyl group, which is a carbonyl group attached to a hydroxyl group.

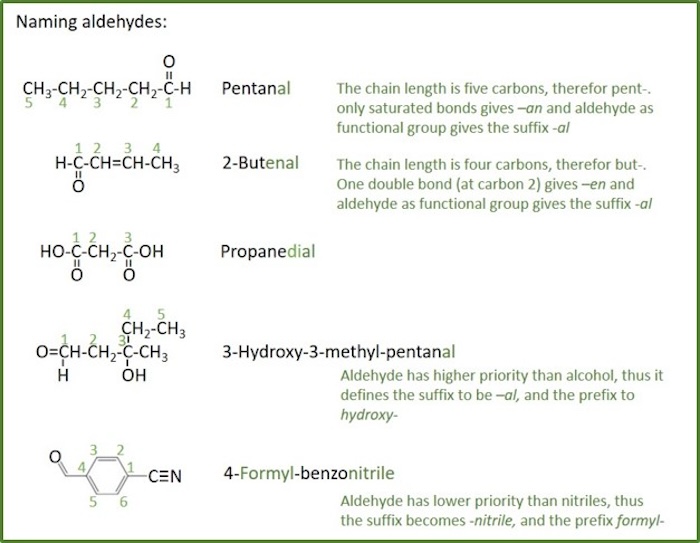
Copyright 2005 by Pearson Education, Inc.Publishing as Benjamin CummingsĪldehydes and KetonesAn aldehyde contains a carbonyl group (C=O), which is a carbon atom with a double bond to an oxygen atom. In an ether, an oxygen atom is bonded to two carbon atoms.

groups that replace a hydrogen atom in the corresponding alkane.a way to classify families of organic compounds.Functional GroupsĪlkenes and AlkynesAlkenes contain a double bond between adjacent carbon atoms.Ĭopyright 2005 by Pearson Education, Inc.Publishing as Benjamin CummingsĪlcohols and EthersAn alcohol contains the hydroxyl (-OH) functional group. Give it a shot to see where you stand.Introduction to Organic Chemistry: AlkanesĮlements in Organic CompoundsIn organic molecules,carbon atoms bond with four bonds.mostly with H and other C atoms.sometimes to O, N, S, sometimes to halogens F, Cl, and Br.įunctional groups area characteristic feature of organic molecules that behave in a predictable way. Ready to test your skills? Each practice is centered on 1 organic compound. Watch the video on how I identified the functional groups present in 3 organic compounds – aspirin, capsaicin and PiCC. If you need to revisit functional groups before attempting to identify multiple functional groups in a compound, do check out my previous post on Introducing the 13 Functional Groups! avoid duplicatesof the same group (ie circle and label only 1 OH group even though there are 3 OH groups in the compound).DON’T split them into 2 groups (ketone & amine) when you see carbonyl group (C=O) right next to N, group it together as an amide.DON’T split them into 2 groups (ketone & ether) when you see carbonyl group (C=O) right next to O, group it together as an ester.exclude alkane (unless specified otherwise by your instructor).scan from top to bottom, or left to right) look for anything that is not C-C single bond in a systematic manner (ie.Are you expected to determine the number of functional groups present in a complex compound? Or perhaps you need to identify the functional groups that are present in a given compound? I have a few tips to share:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
